Reflection Blog 3
After reading through a milieu of research papers about Neurofibromatosis Type I (NF1), breaking down the disease from the miniscule atomic level to the macroscale organs systems level, I have obtained a clearer view of how to organize all relevant information. To present NF1 in a digestible manner, I will divide my website up into 5 main pages (not including the home page): 3 pages about the disease, 1 page about the healthy state, and 1 page dedicated to the annotated bibliography. The pages will be split thematically in the following way:
- Disease Discovery and Clinical Manifestations
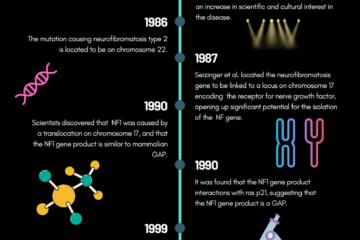
- The extreme clinical manifestations of NF1, sadly, have made patients throughout history subject to humiliation and discrimination because of the phenotypes associated with the disease. The history of NF1 is rooted in outcasting and shame. One of the major reasons for the rise of NF1 to academic relevancy was the cultural spotlight placed on Joseph Merrick, more commonly known as the Elephant Man, in the late 19th Century. Furthermore, early writings of NF1 described patients of the disease as “monsters.” The context that those descriptions were written in (Renaissance Europe) requires deeper scrutiny into the validity of the reports. Furthermore, the clinical manifestations of NF1 are, although usually severe, quite variable. Therefore, it is worth discussing the various clinical manifestations of the disease along with the social context it must be understood within before delving into the scientific literature on the disease.
- Mutations & Proteins
- Similar to the previous discussion on phenotypic variability, there is a similar amount of genotypic variability with NF1, and this variability is not correlated with severity of disease! Discussing the various genetic factors that may lead to NF1 will provide a good foundation for the discussion of the proteins that are mutated in NF1, mainly, neurofibromin. I will discuss the discovery, structure, and function of neurofibromin. Additionally, I will explain how mutations in neurofibromin impact its function, leading to NF1.
Scientific Innovations:
- Site-Directed Mutagenesis
- X-Ray Crystallography
- Cryo-EM
- Recombinant DNA Technology
- Cells & Pathways
- The extensive effects and various phenotypes of NF1 likely arise due to the multitude of crucial regulatory and signaling pathways that are affected by the disease. A discussion of the primary cells affected by NF1 will provide insight into the location of the disease within the body, what organ systems it affects, and how. Furthermore, a discussion of the pathways affected by NF1 will illuminate the specific ways that NF1 exerts its influence on the body at the cellular and subcellular levels, specifically having to do with cellular signaling, and the regulation of cell growth, specialization, and differentiation.
Scientific Innovations:
- Western Blot
- Bacterial transfection
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
- Immunocytochemistry
- Immunohistochemistry
- Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
- Treatment, Disease Progression, and the healthy state
- Sadly, this may be the briefest section out of the 4 previously discussed. Due to the complexity and variability of the disease, there are not too many known methods of treating or preventing NF1. However, the disease is not significantly lethal, therefore, much of this page will be devoted to discussing the “normal” progression of the disease, and how patients are instructed to manage their symptoms. Interspersed throughout my discussion of treatment, the healthy state of the affected proteins, pathways, and cells will be elaborated upon further, in order to gain a better conception of the biochemical depth of the disease.
0 Comments